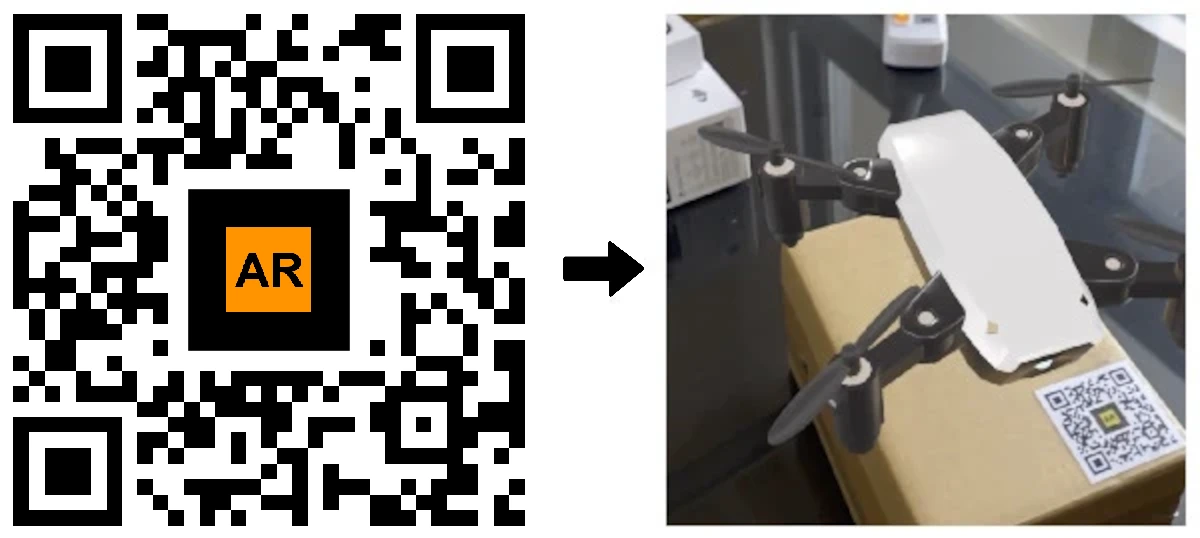
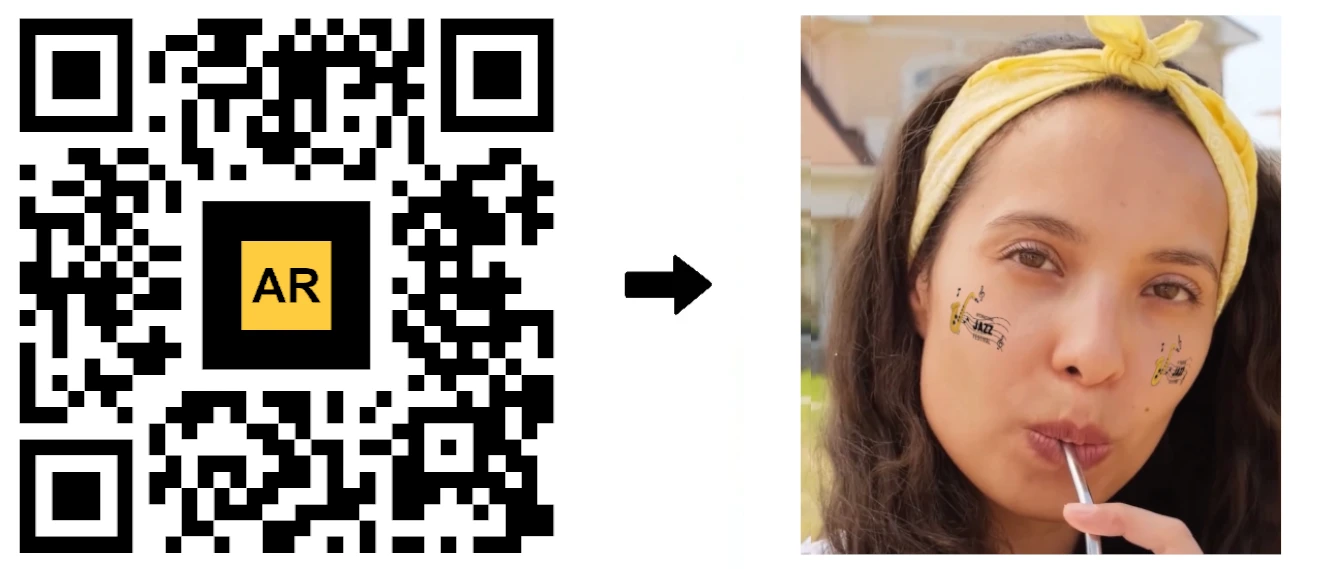
What is the difference between a QR Code and an AR Code?
AR Code Tech | 01/03/2026 |
Since the early 2000s, QR Codes have powered digital marketing, mobile payments, and information exchange. The AR Code SaaS platform lets your business transform standard QR Codes into dynamic AR experiences, helping you stand out with immersive augmented reality content that drives customer engagement and brand recall.
The Evolution of the QR Code
Invented in 1999 by Masahiro Hara of Denso Wave, QR Codes began as a reliable industrial tracking tool. They rapidly gained popularity across Japan and soon achieved global adoption, thanks to widespread mobile device integration and ongoing technological innovation.
Modern smartphones make it easy for consumers everywhere to interact with both QR and AR Codes. Learn how to scan AR Codes on any smartphone and access interactive AR experiences within seconds.
In Asia, QR Codes have revolutionized payments, social networking, interactive advertising, and streamlined data handling. Businesses worldwide now leverage QR Codes for digital sales, social sharing, and next-generation augmented reality brand content, cultivating real connections between physical products and digital experiences.
Upgrade Your Marketing: Transform QR Codes into AR Codes
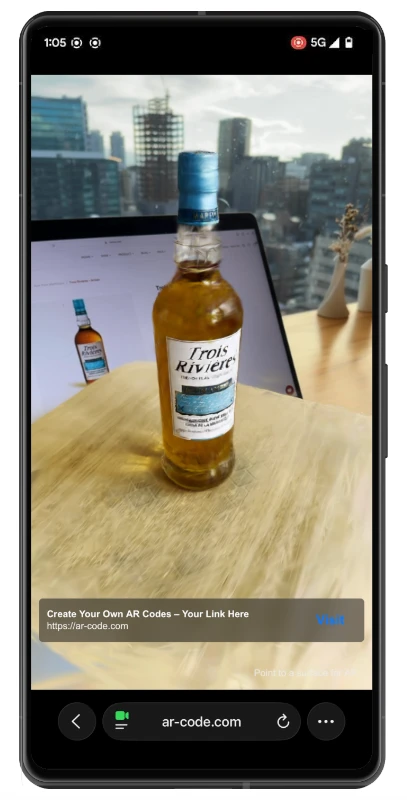
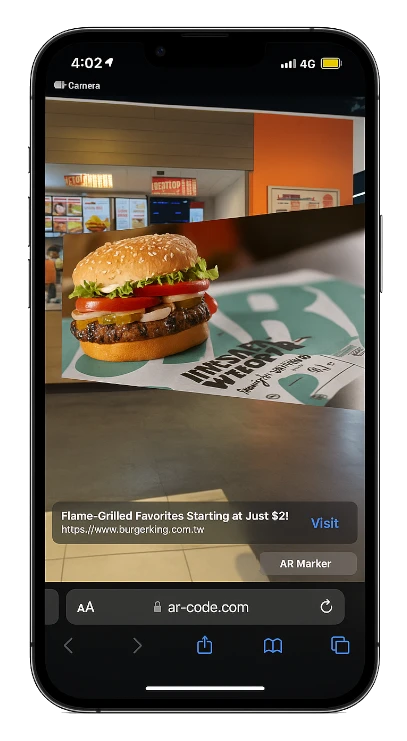
Modern customers demand more than traditional QR interactions. With AR Codes, your business can deliver engaging augmented reality on packaging, print, and in-store displays, promoting direct interaction and higher conversion rates. Discover AR Codes on product packaging to maximize your marketing impact.
Technologies such as Apple App Clips and WebAR empower businesses to launch interactive AR experiences directly from physical materials, grabbing consumer attention and encouraging immediate engagement.
Turn QR codes into AR-powered shopping, interactive demos, and immersive branded storytelling. AR Codes offer scalable solutions for business growth and customer loyalty.
Emerging AR tech, such as Apple Vision Pro Codes, is changing the way organizations connect with customers. Apple App Clips create instant digital access, while the Vision Pro headset provides an immersive AR environment. Explore our QR Code vs AR Code comparison to optimize your brand’s strategy.
What is Augmented Reality and Why is it Critical for Your Business?
Augmented Reality (AR) integrates 3D models, videos, images, and information into the real environment, making your brand’s content interactive and memorable. AR is proven to drive customer engagement and differentiate your products in competitive markets.
The AR business ecosystem brings together:
-
AR Device: Over 2 billion smartphones support AR, with adoption of AR glasses accelerating. Major companies invest in AR development, leveraging platforms like ARKit and exploring the business potential of the metaverse.
-
AR Content: Interactive AR content can transform gamification, employee training, and customer engagement. Microsoft Hololens 2 leads in enterprise AR. Discover real estate applications of AR Codes for virtual tours and stronger leads.
-
AR Render: Realistic rendering is vital for marketing, sales, and training. WebAR offers AR via the web, removing the hassle of app installs. ARKit and ARCore power global AR deployment for businesses of all sizes.
-
AR Anchoring: Discover anchoring options to optimize AR engagement:
- Direct Environment Anchoring: Attach AR content to real spaces for interactive experiences on location.
- Geolocation Anchoring: Deliver location-triggered AR campaigns. See how smart cities use AR Codes to engage communities.
- Object Recognition Anchoring: Leverage WebAR for live AR on products and faces.
- Ultra-wideband Anchoring: Use precision tracking for impactful product visualization, inspired by Apple AirTag innovations.
- AR Codes Anchoring: Instantly launch AR by scanning AR Codes on products or displays for seamless digital-physical integration.
With dynamic anchoring, 3D content, and state-of-the-art rendering, AR Code accelerates your business’s digital transformation. Launch AR demos, marketing, and training instantly using our AR Cloud API.
Boost Customer Engagement with AR Codes
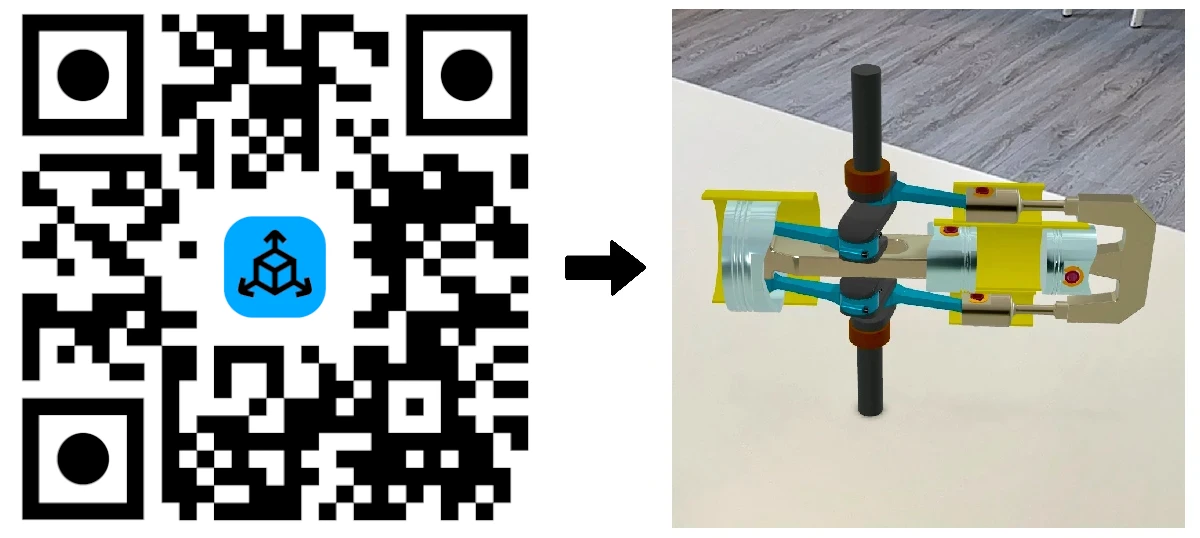
AR Codes connect your offline assets with interactive online experiences in a single scan. Engage customers with 3D product demos on packaging, deliver on-the-spot AR instructions on printed materials, and supercharge advertising with interactive AR previews that increase conversions. AR Code SaaS supports 3D File Upload, Object Capture, AR Face Filter, and AR Video. Follow our AR photo guide or watch our video to create 3D text for AR to get started. For fast and efficient 3D AR experiences, use the new AR GenAI solution to generate a 3D AR experience from a single photo of your object.
AR Code SaaS: 4 Types of AR Rendering Solutions
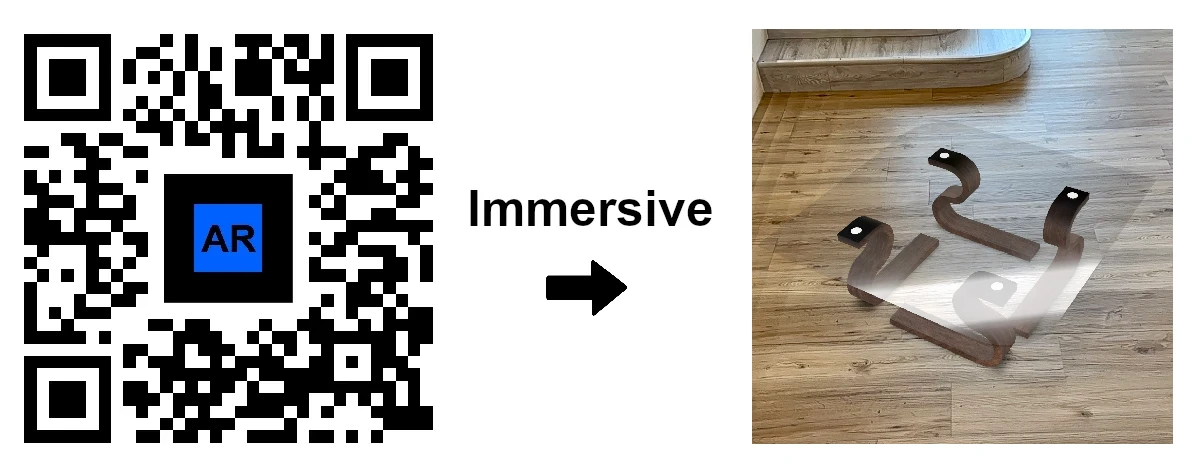
Immersive AR: Deliver interactive 3D product experiences, allowing customers to explore your offerings in real time.
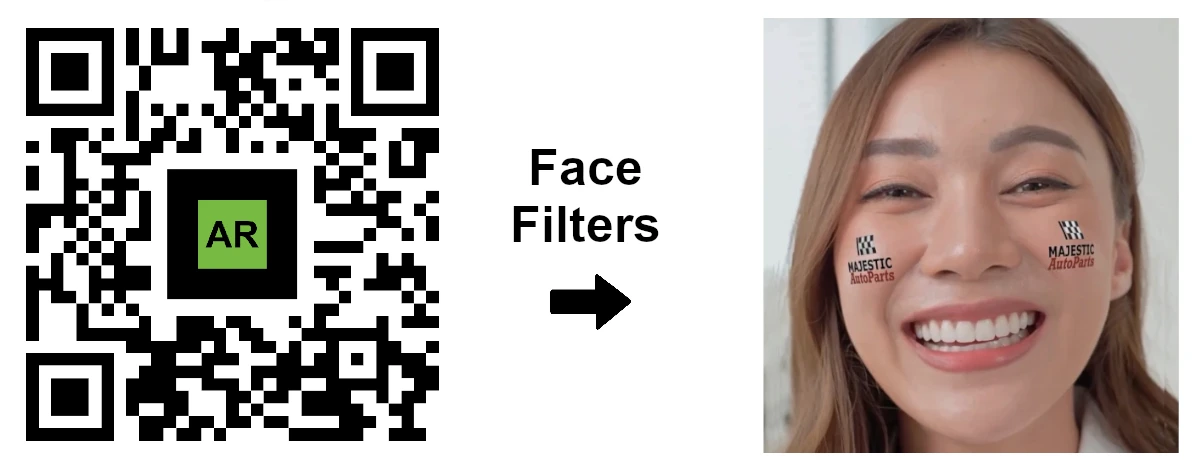
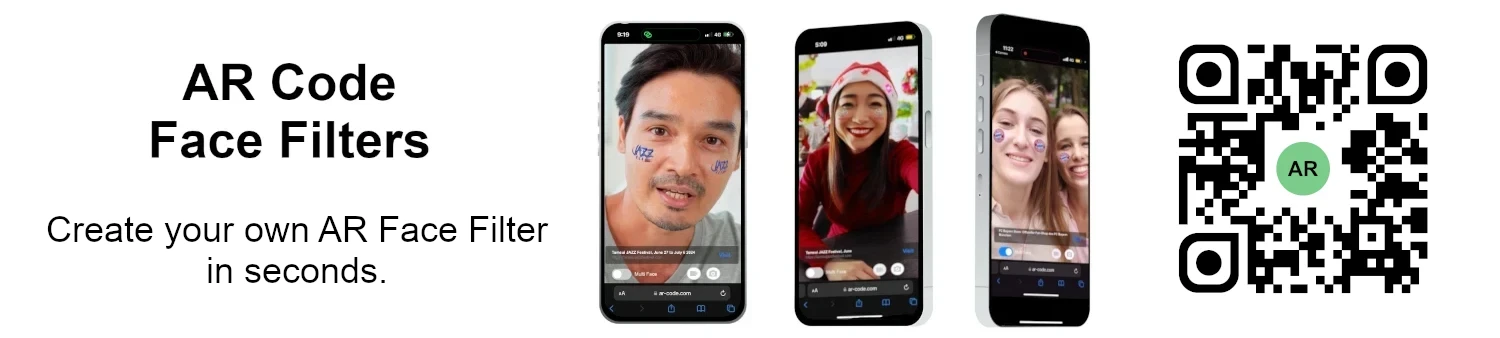
Face Filters AR: Boost brand visibility and social media reach with custom AR face filters for your campaigns.
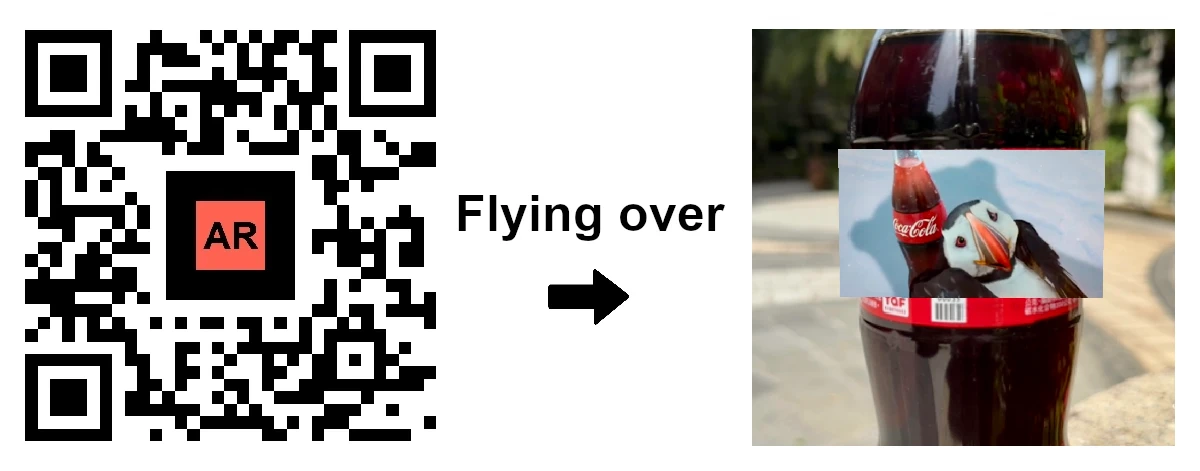
Flying Over AR: Project floating 3D models or videos above AR Codes for high-impact, memorable marketing.
AI Assistance AR: Enhance user interactions with AI Code for smart image analysis and personalization that builds customer loyalty.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are QR codes and how did they originate?
QR Codes originated with Masahiro Hara at Denso Wave in 1999 as a fast, open-licensed way to store data for industrial use, and quickly spread to other sectors. See our QR vs AR Code business guide for more.
What are App Clips Codes?
App Clips Codes are Apple’s QR codes that let users quickly launch mini-app AR experiences, providing direct access to services and content on iPhone or iPad.
What are AR Codes and how do they relate to QR Codes?
AR Codes build on QR codes by unlocking interactive augmented reality experiences, beyond simply linking to web pages. Explore our AR Code SaaS overview and discover how marketing agencies use AR Codes to deliver next-level engagement for business clients.
AR Code Tech - Latest Blog Posts
AR GenAI: Turn a Single Photo into an AR-Ready 3D Model

Unlock the power of AR GenAI, the groundbreaking Image to 3D solution from AR Code, now live within the AR Code SaaS platform. With AR GenAI, businesses can convert a single product photo into an interactive 3D model for instant display in Augmented Reality. There is no need for app downloads, 3D scanning, or expert...
AR Splat: A New 3D Scanning-to-Augmented Reality Solution Based on Gaussian Splatting

AR Splat by AR Code is the all-in-one SaaS solution for businesses seeking fast, immersive 3D content creation through web-based augmented reality. By uploading a simple walk-around video, AR Splat instantly generates a photo-realistic 3D scene using cutting-edge Gaussian Splatting technology. Each 3D scene is...
AI Code’s Image Generation Redefines Product Visualization Through a QR Code Scan
AR Code revolutionizes Augmented Reality (AR) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for businesses with instant AI-generated visualizations accessible through a simple QR code scan. Maximize engagement with AI Code for your business and boost customer interaction using immersive, web-based AR experiences on any...
AR Code Object Capture Now Works on All iPhones and iPads No LiDAR Required
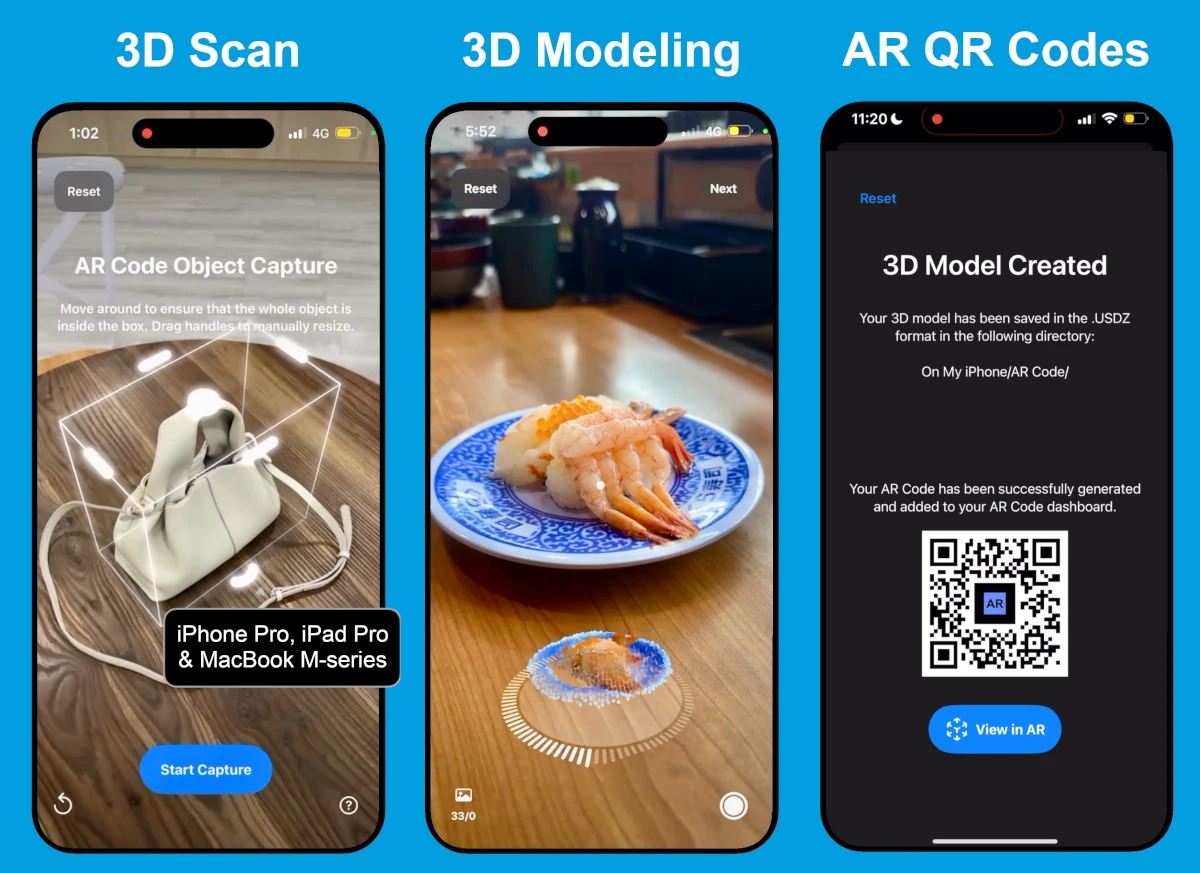
Supercharge your business with immersive augmented reality using the AR Code Object Capture app. Seamlessly capture and create 3D models along with AR QR Codes on any iPhone or iPad—no LiDAR necessary. Simplify digital workflows, boost customer engagement, and deliver interactive AR marketing, support, and product...
3D Scanning from Video Now Available on the AR Code Web Interface
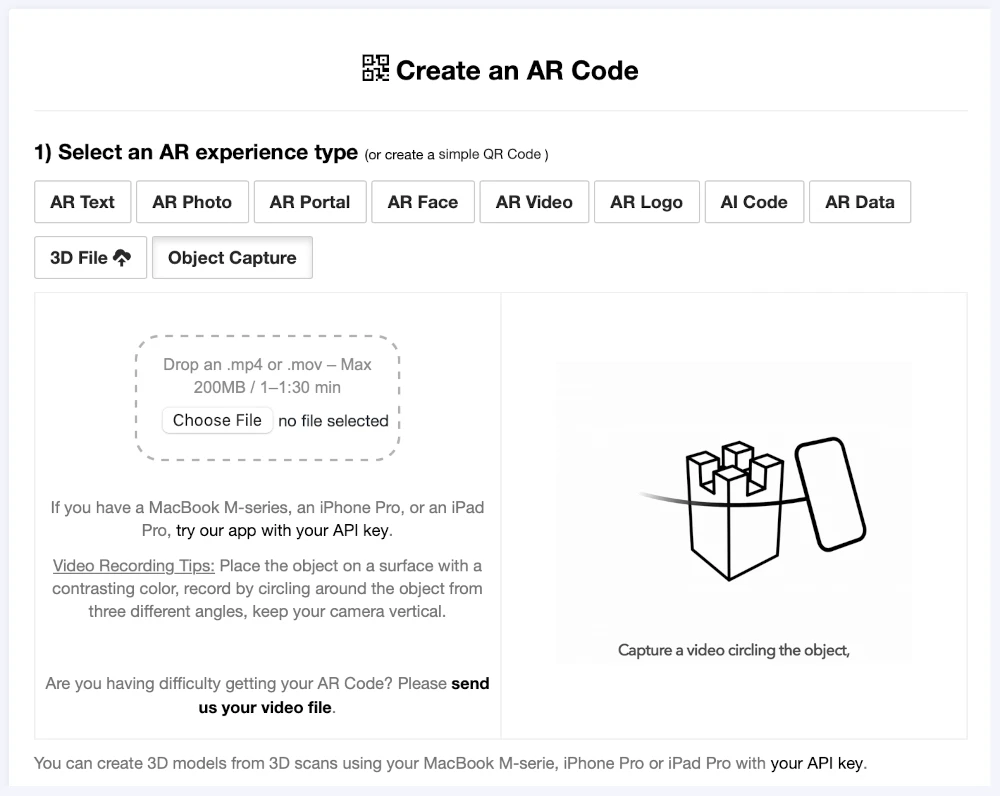
Propel your business into the next era of digital engagement with the advanced AR Code Object Capture solution. Hosted on our web platform, AR Code empowers companies to create immersive augmented reality content from simple video-based 3D scans. Transform brand engagement and streamline workflows without...
Guide to 3D Scanning with Our "AR Code Object Capture" Solution

Accelerate your business’s digital transformation with AR Code Object Capture, a powerful SaaS platform for 3D scanning and immersive augmented reality experiences. Trusted by leading organizations, AR Code delivers precise 3D model creation for marketing, e-commerce, manufacturing, and engaging product demos....
From Video to 3D Modeling: Photogrammetry with AR Code Object Capture on MacBook M-Series
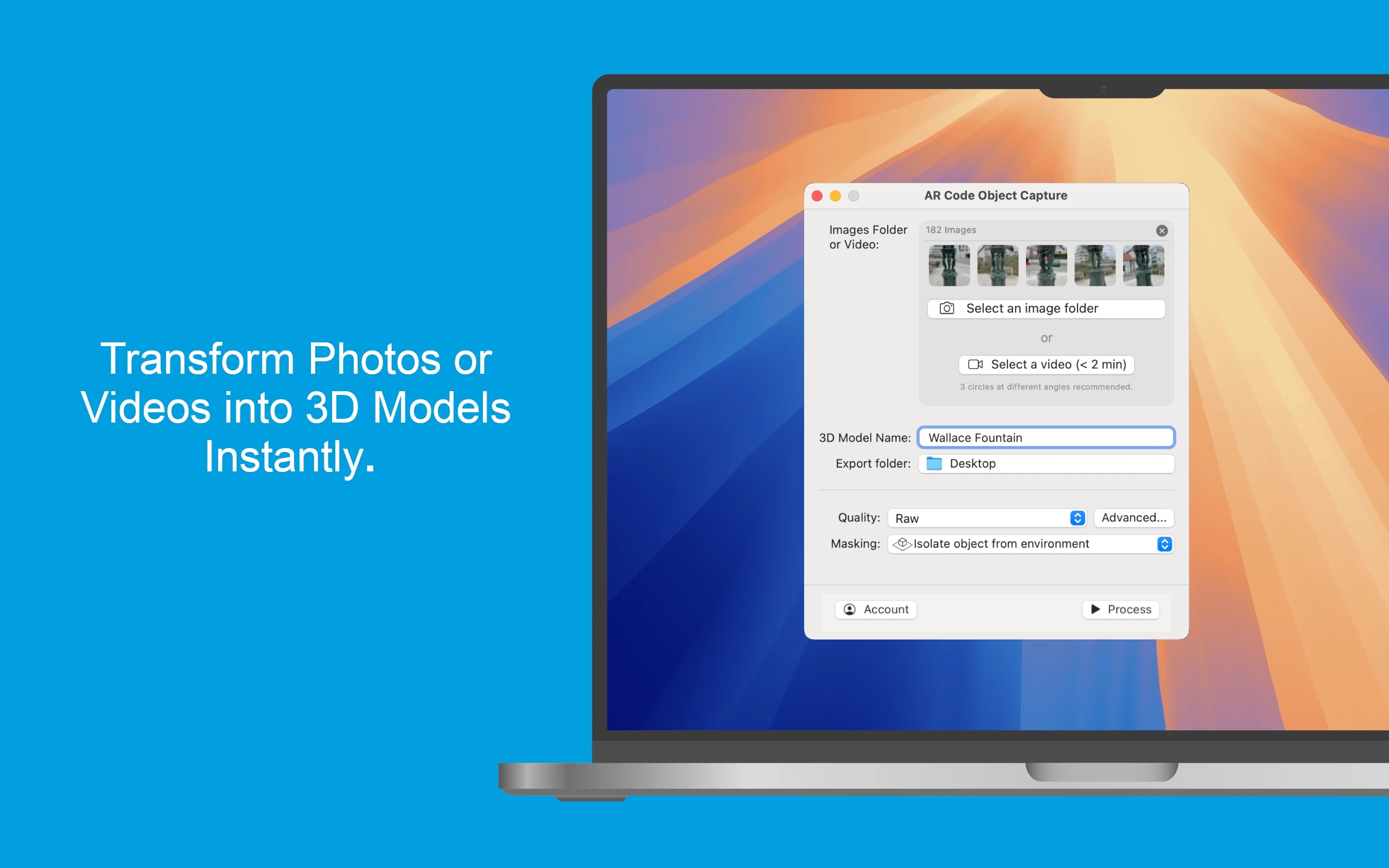
Empower your business growth with the innovative AR Code Object Capture app, the ultimate 3D scanning and augmented reality SaaS platform for enterprises. Purpose-built for MacBook M-series (macOS 15.0+), this app transforms physical products into engaging 3D models and AR QR Codes within minutes. Effortlessly sync...
Personalize Your AR Codes with Innovative Design Options
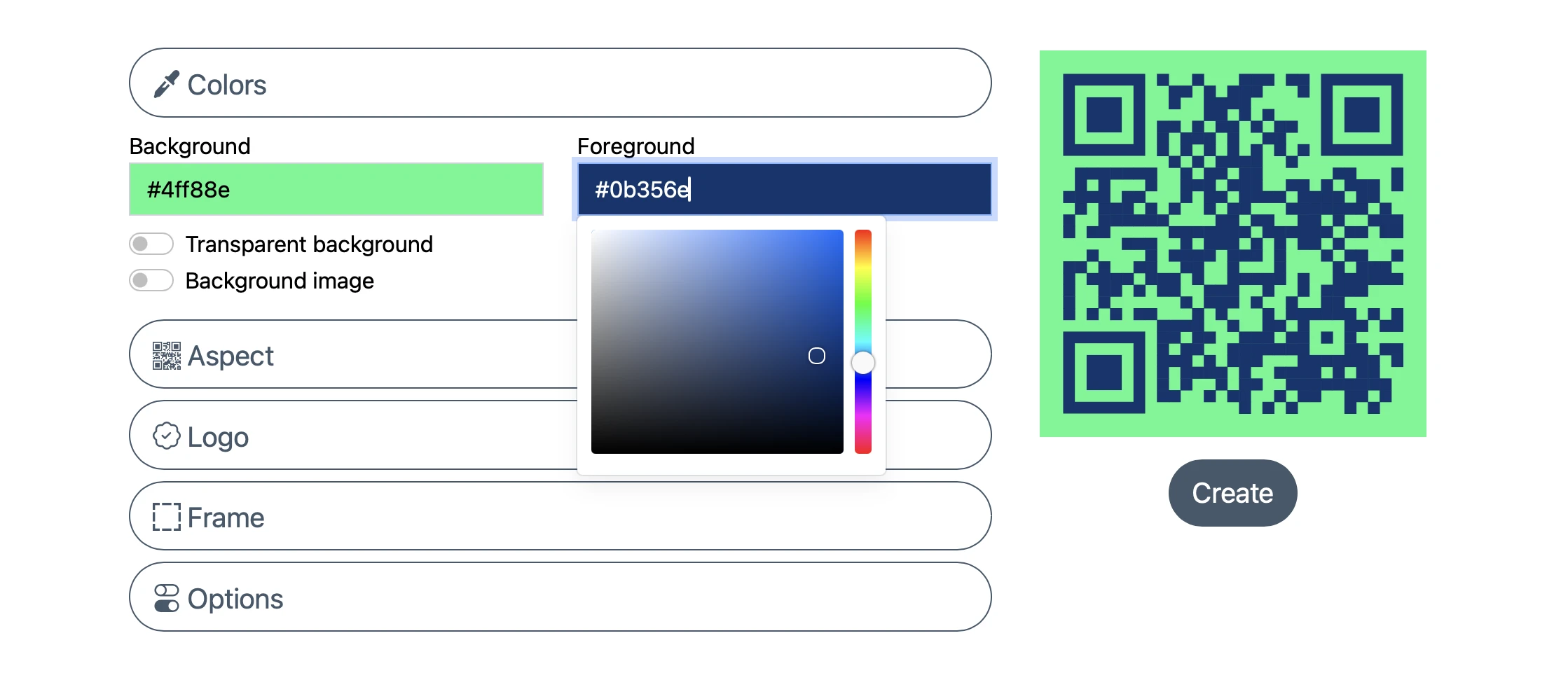
AR Codes are transforming how businesses engage customers by bridging physical products, printed materials, and digital content into dynamic augmented reality experiences. On the AR Code SaaS platform, AR Codes go beyond traditional QR codes with advanced visual customization. These next-generation codes become...
AR Code's Low-Power SLAM: Augmented Reality for Everyone, Everywhere
Accelerate your business growth with AR Code, the leading SaaS platform for web-based Augmented Reality. AR Code empowers companies to deliver dynamic AR experiences accessible on any device, from premium smartphones to budget Android models. Using advanced low-power SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)...
Revolutionize Your Online Boutique with 3D Scans Using the AR Code Object Capture App

In today's evolving e-commerce market, delivering immersive, interactive shopping is essential for brands to thrive. Shoppers now expect to experience products virtually as vividly as in-store. AR Code empowers businesses to exceed expectations with cutting-edge Augmented Reality solutions. Through the intuitive AR...
167,886 AR experiences
587,778 Scans per day
133,859 Creators